How to Configure Your Danfoss Piston Pump

Danfoss piston pumps are renowned for their reliability, efficiency, and adaptability to various hydraulic systems, making them a top choice for many industrial applications. However, if these pumps aren’t correctly configured for the application, there will be performance issues and an overall decline in their lifespan.
Configuration options will vary depending on the piston pump’s model/series. However, there are a few customizable elements that apply to most Danfoss piston pumps.
In this article, we’ll look at some of these elements and provide guidance on configuring each element to meet your needs.
Displacement Rate
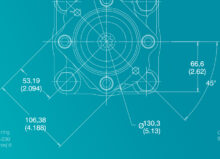
Displacement rate refers to the volume of fluid that the pump can displace per cycle or rotation—it’s usually measured in cubic inches or centimeters. Each Danfoss pump series has varied displacement rates.
To determine your displacement rate, you must evaluate your hydraulic system’s flow rate requirements (higher displacement rates yield higher flow rates) and match the displacement rate to your system’s pressure requirements.
Rotation
You can typically choose between two rotation types: left-hand (counterclockwise) and right-hand (clockwise). The choice boils down to your system’s design and the spatial configuration of other components.
Most systems are designed for right-hand rotation. However, some specialized applications, like compact assemblies or systems intended for specific directional processes, may need left-hand rotation to minimize interference or spatial constraints.
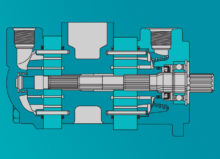
Shaft Options
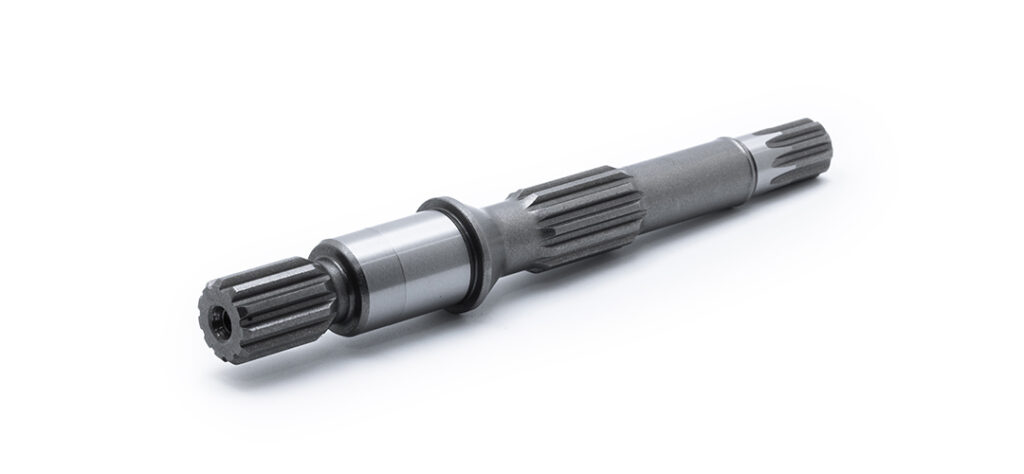

Next, you’ll need to choose between splined, keyed, or tapered shafts. Splined shafts provide more contact points between the shaft and the mount, which is beneficial for transmitting higher torques and for applications where alignment is critical. Splined shafts are recommended for dynamic, high-load environments.
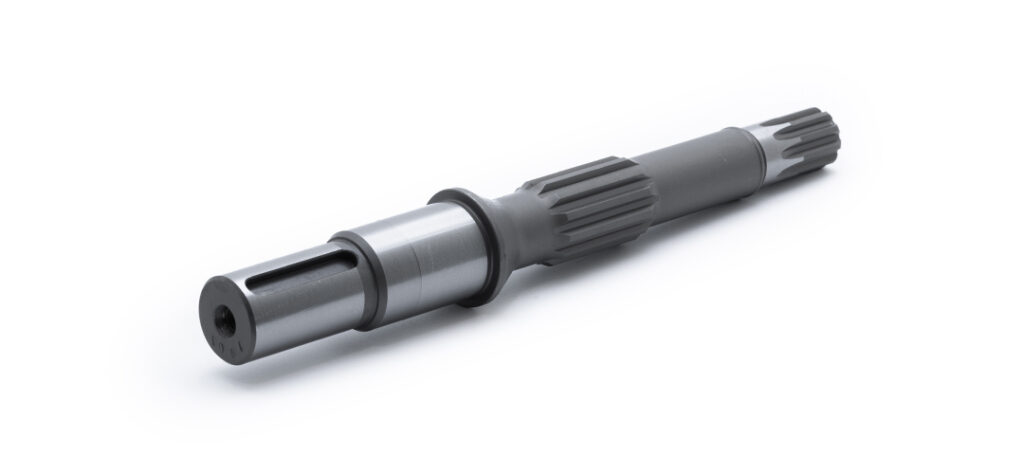

Keyed shafts are easier to install and maintain. They’re generally adequate for applications where torque requirements are moderate and cost or simplicity is a priority.
Lastly, tapered shafts are recommended for applications that require high-torque transmission and precise alignment because they provide a secure fit by wedging tightly into the mating component.
Port Location
There are generally two choices: side and rear. Side ports make maintenance easier and are chosen for applications with more convenient side access. Rear ports are used for pumps mounted in tight spaces or when a more compact setup is required.
Control Options
Variable displacement pumps often feature control options, including:
- Pressure Compensator: Automatically adjusts the pump’s output to meet specific pressure requirements.
- Pressure & Flow Compensator: Combines pressure and flow control.
- Torque Sensing: Modifies pump displacement based on the torque demand.
- Electronic Proportional Control: Controls pump operations via electronic signals; ideal for applications that need precise control.
- Manual Displacement Control: Allows operators to adjust displacement manually and is often used in applications where electronic control isn’t feasible.
- Hydraulic Remote Control: Operates the pump through a remote hydraulic signal.
- Forward-Neutral-Reverse Control: Provides directional control of the pump’s output and is often used in systems that need reversible operation.
Get Help Configuring Your Piston Pump
Founded over 25 years ago, Panagon Systems manufactures OEM-equivalent piston pumps from brands like Danfoss. We can manufacture all types of Danfoss closed-and open-circuit piston pumps, including PVXS, PVXF, PVWS, PVH, PVQ, PVM, and more.
Please contact us today with your configuration questions. Our product specialists can help you identify and configure the right pump for your application.