What Is a Power Take-Off?

A power take-off (or PTO) is a mechanical device that “takes off” power from the engine, meaning that it allows an engine to transfer its power to another piece of equipment, usually a machine or attachment that exists separate from the engine itself (think of the blade mechanism on a snowplow or a dump truck lifting its tailgate).
PTOs are commonly found on trucks, tractors, and other large pieces of engine-driven equipment and are typically installed on the flywheel or other parts of a vehicle’s engine or on the transmission. Because PTOs can integrate directly with the engine, they eliminate the need for an additional secondary engine that would otherwise be necessary to power any external equipment pieces.
Types
Mechanical
Mechanical power take-offs rely on a lever or switch for engagement. Some common types of mechanical PTOs are transmission-mounted, engine-mounted, and split-shaft. Transmission-mounted PTOs are attached to the transmission, engine-mounted to the engine, and split-shaft PTOs to the driveline. Transmission PTOs tend to be the most common type of mechanical PTO.
Hydraulic
Hydraulic power take-offs are usually found on automatic transmissions, in which power is transferred from the vehicle engine to a hydraulic pump or other component. Generally speaking, hydraulic PTOs are considered smoother and easier to engage than mechanical models. They may be found in everything from construction vehicles to farming equipment.
Electric
Electric power take-offs rely on an electric motor and inverter to power auxiliary functions. Electric PTOs, or ePTOs, use direct current as the main power source, similar to a battery, to create power. Some of the key benefits of an ePTO include reduced emissions, cost efficiency, and improved performance compared to other types of PTOs. However, ePTOs tend to have a higher upfront cost and may have a limited battery range. ePTOs are often found in construction vehicles, sanitary vehicles, or in hybrid or electric vehicles.
Front-Mounted
Front-mounted power take-offs work by getting energy directly from the engine’s crankshaft. With these types of PTOs, a driveline runs from the engine to the equipment the PTO is intended to power. Front-mounted PTOs are popular in snow removal applications for powering the blade mechanism that clears roads and lots.
Rear-Mounted
Rear-mounted PTOs, or countershaft power take-offs, typically attach to the transmission and are powered by the countershaft. While rear-mounted PTOs aren’t as common as other types, some of the advantages that they offer include easier installation, higher overall torque limits, and better compatibility with certain pumps and other applications. Rear-mounted PTOs are often found on dump trucks, cement mixers, and small cranes.
Side-Mounted
Side-mounted power take-offs are popular on trucks and mounted right on the side of the main transmission. Because of the location, side-mounted PTOs are designed to interact directly with the transmission gear and are often installed on dump trucks, utility vehicles, and other heavy-duty vehicles.
Common Issues
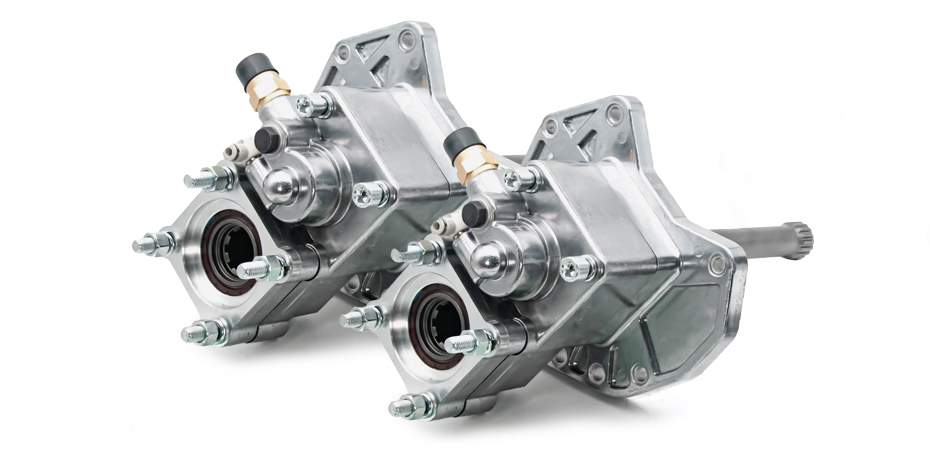

Some of the most common issues people experience with PTOs include:
- Excessive noise and vibration coming from the PTO, which are often the result of worn bearings, misaligned gears, or other loose components.
- Damaged splines from improper engagement.
- Seal failures or bad gaskets that can lead to leaks.
- Difficulty engaging and disengaging, which is often due to a bad solenoid or a stuck clutch.
- Excessive heat generation from low oil levels, poor lubrication, or an excessive load being placed on the PTO.
The best way to troubleshoot some of the common issues with PTOs is to ensure you’re properly maintaining them. Look for visible signs of damage, make sure oil levels are adequate, and conduct tests that check for proper engagement and disengagement.
Find More Resources at Panagon Systems
Panagon Systems is a U.S.-based manufacturer of aftermarket hydraulic pumps, motors, and other replacement parts. Please visit our blog for more resources related to hydraulics systems, pumps, motors, and more.